Get a monitor and contributor to air quality data in your city.
274.8K people follow this city





AIR QUALITY DATA CONTRIBUTORS
Find out more about contributors and data sources| Index | Very high | ||
| Tree pollen | Very high | ||
| Grass pollen | None | ||
| Weed pollen | None |
| Weather | Clear sky |
| Temperature | 68°F |
| Humidity | 52% |
| Wind | 8.1 mp/h |
| Pressure | 30.2 Hg |
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  Düsseldorf, Nordrhein-Westfalen Düsseldorf, Nordrhein-Westfalen | 64 |
| 2 |  Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | 64 |
| 3 |  Augsburg, Bavaria Augsburg, Bavaria | 60 |
| 4 |  Leipzig, Saxony Leipzig, Saxony | 58 |
| 5 |  Duisburg, Nordrhein-Westfalen Duisburg, Nordrhein-Westfalen | 57 |
| 6 |  Essen, Nordrhein-Westfalen Essen, Nordrhein-Westfalen | 57 |
| 7 |  Köln, Nordrhein-Westfalen Köln, Nordrhein-Westfalen | 56 |
| 8 |  Munich, Bavaria Munich, Bavaria | 55 |
| 9 |  Nuremberg, Bavaria Nuremberg, Bavaria | 54 |
| 10 |  Osnabrueck, Lower Saxony Osnabrueck, Lower Saxony | 54 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hamburg HafenCity | 38 |
| 2 | Flughafen Nord | 34 |
| 3 | Sternschanze | 34 |
| 4 | Hamburg Bramfeld | 33 |
| 5 | Neugraben | 32 |
| 6 | Fliesenzentrale | 27 |
| 7 | Mellingstedt | 27 |
| 8 | Hamburg Harburg | 22 |
| 9 | Bramweg | 16 |
| 10 | Uhlenhorst Schone Aussicht | 16 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
34
live AQI index
Good
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 34 US AQI | O3 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 4.5µg/m³ | |
| O3 | 83.5µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 9µg/m³ | |
| SO2 | 3µg/m³ | |
| CO | 100µg/m³ | |
PM2.5 concentration in Hamburg City air currently meets the WHO annual air quality guideline value
| Enjoy outdoor activities | |
| Open your windows to bring clean, fresh air indoors GET A MONITOR |
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wednesday, May 8 | Good 28 AQI US | 64.4° 41° | ||
| Thursday, May 9 | Good 42 AQI US | 66.2° 44.6° | ||
| Friday, May 10 | Moderate 52 AQI US | 66.2° 46.4° | ||
| Today | Good 34 AQI US | 68° 48.2° | ||
| Sunday, May 12 | Good 39 AQI US | 66.2° 44.6° | ||
| Monday, May 13 | Good 45 AQI US | 69.8° 46.4° | ||
| Tuesday, May 14 | Good 46 AQI US | 71.6° 48.2° | ||
| Wednesday, May 15 | Good 49 AQI US | 71.6° 51.8° | ||
| Thursday, May 16 | Good 37 AQI US | 69.8° 51.8° | ||
| Friday, May 17 | Moderate 78 AQI US | 69.8° 50° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
The average fine dust value PM2.5 of Hamburg, the second largest city in Germany, was 10.8 µg/m3 according to the 2019 city ranking. Thus, in 2019, the WHO recommended levels of the concentration of PM2.5 in Hamburg was exceeded by .8 µg/m3. However, the PM2.5 value is "good" according to the less stringent air quality index (AQI) of the Federal Environment Agency.
Over a period of six months, Hamburg attained the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) air quality guideline value of 10 µg/m3 for PM2.5 in 2019. The worst air quality was recorded in Berlin during March and December 2019.
Compared to Munich, which is another major German city, Hamburg's PM2.5 value was around 2% worse. Overall, Hamburg ranks 75th among the municipalities in Germany with the worst air quality. The highest air pollution was measured in Giessen, with an average value of 14.9 µg/m3. Compared to Europe's largest port city Sines in Portugal, which had an average PM2.5 value of 6.8 µg/m3 in 2019, Hamburg had much worse air quality. The other major port cities of Rotterdam in the Netherlands and Antwerp in Belgium had an average PM2.5 value in 2019 of 11.2 µg/m3 and 12.9 µg/m3 respectively.
The impact on air quality is particularly noticeable in the city centre due to intensive industrial production, urban traffic and the central port location. The air quality north of the Elbe River in Hamburg is mainly influenced by wood-burning and general heating practices of private households. This pattern of air pollution also shows a correlation with the population density in the area. Particulate matter pollution from ships’ engines is particularly noticeable near the port and along the Elbe River. Higher levels of particulate matter can also be found around the Alster River. In winter, air pollution from PM2.5 is 60% higher, due to more intensive heating behaviour of Hamburg's city residents and the corresponding weather conditions.
Hamburg airport is also a cause of air pollution. Airport authorities state that most air pollutants come from internal vehicle operations, not from air traffic itself. This includes the maintenance and movements of aircraft on the ground. Hamburg Airport is currently endeavouring to make its energy management more efficient and to make greater use of renewable and more environmentally friendly energy sources.
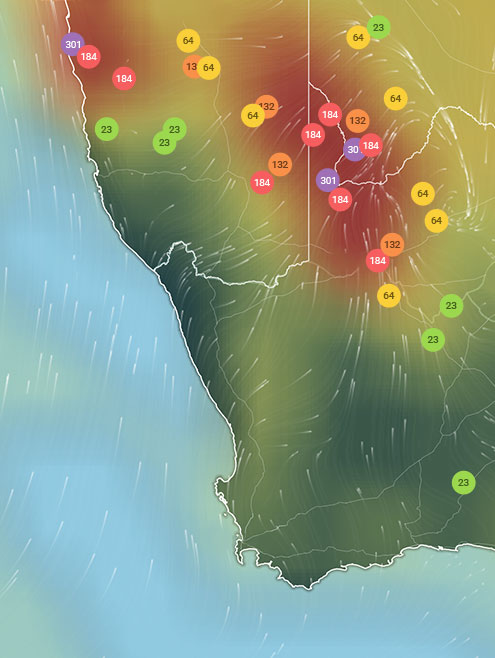
To see the exact air pollution in certain parts of Hamburg, the real-time map is located at the top of the IQAir.com website. This live data makes it possible to keep an eye on the air quality in Hamburg and the surrounding area.
The Hanseatic City of Hamburg is home to the largest port in Germany. Due to the high level of shipping traffic at the port of Hamburg, this district is badly affected by air pollution. However, it is not only marine vessels that contribute to air pollution, but also the increase in heavy transport used for the transportation of goods both to and from the port. Although the annual average values for nitrogen oxides (NOx) appear to have been kept within the limits, according to EU legislation. Although there are isolated cases when the figure has exceeded the recommended levels, which can be a major source of aggravation for sensitive groups. Occasionally, these high levels of exposure last for a whole month. The measurements are carried out independently by the Nature and Biodiversity Conservation Union (NABU) and show higher values compared to the official figures of the Hamburg Senate.
The air pollution in Hamburg has several main sources.
Road traffic is one of the largest sources of air pollution in Hamburg. Cars are the main contributors to the pollution of Hamburg's air, closely followed by commercial vehicles and trucks. According to the forecasts of the Institute of Shipping Economics and Logistics (ISL), emissions are expected to decrease in the coming years due to the progressive development of new technologies.
Another major source of air pollution in Hamburg comes from shipping, first and foremost from container ships, followed by tankers. Nearly all of the nitric oxide (NOx) present here is caused by the combustion processes in ships' engines and is significant in numbers. The release of these emissions usually occurs during the time when the ships are in port. According to a forecast by the Institute of Shipping Economics and Logistics (ISL), nitric oxide (NOx) emission levels will continue to rise until 2025 and thus continue to pollute the air quality of the City of Hamburg.
Another significant source of pollution is the emissions from industry in Hamburg. This primarily includes combustion plants with various fuels and emissions produced through waste disposal and incineration. In addition, there are emissions from the processing and production of crude oil and metals. Combustion in households and small businesses, such as wood-burning, also contributes to the emissions.
During the colder winter months, air pollution tends to increase. This rise is related to the increased heating behaviour of Hamburg's city residents and the air pollutants emitted as a result. In addition, the winter inversion weather situation also plays an important role, as the cold, heavy layer of air is trapped under the warm, lighter layer. Due to this blockage, there is hardly any air circulation between these two layers and the air pollutants become trapped under the warm air. As a result, increased levels of pollutants are measured and the air quality index (AQI) tends to be "moderate" in the affected months.
In the Hamburg municipality, air pollutants can impair the health of sensitive people. Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and fine dust particles (PM2.5 and PM10) are the main contributors to health problems. The health effects can be felt through cardiovascular problems, respiratory problems, asthma, bronchitis and coughing. Exposure also increases the likelihood of developing lung cancer or respiratory infections. In addition, high levels of air pollution can lead to a reduction in life expectancy. Furthermore, children often suffer from impaired lung function.
The anthropogenic effects of air pollutants on the environment are also evident in the strong acidification and eutrophication of the soil in Hamburg and its surroundings. The high pH value is related to increased nutrient levels in the soil, which in turn can have a negative impact on the fauna and the general ecosystem of the environment. To counteract this, not only must air pollution be reduced, but direct measures must also be taken to help the soil.
In 2017, the City of Hamburg's Ministry of Environment and Energy published a revised version of the Clean Air Plan with a focus on the links between the various procedures. The first package of measures of the city state of Hamburg concentrates on an expansion of the local public transport system (ÖPNV). This first package is followed by measures to increase the use of bicycles and electric transport. Through expanded management and improved logistics, the general traffic situation is also to be improved and the mixed use of passenger and public transportation is also to be simplified. This should significantly reduce traffic and thus air pollution on Hamburg's roads.
In order to reduce private and commercial incineration, subsidy programmes are to come into force that support renovations or improved insulation techniques. A general expansion of renewable energies, through the extended use of wind and solar energy, is also included in this package of measures.
The Clean Air Plan of the City of Hamburg only deals with nitrogen dioxide (NO2) emissions, but not with other air pollutants that are in the Hamburg air. The responsible persons justify this by stating that the other pollutants remain within the recommended limits. This means that they are not legally obliged to draw up or renew an air pollution control plan for other air pollutants such as PM10.
The city of Hamburg last published an action plan against fine dust pollution in 2005. This plan was drawn up due to the fact that on several occasions, the limits had been exceeded in the Habichtstraße during the previous 15 months. The occurrences can be traced back to, not only local city traffic at the measuring point but also to regional background values which also influence the high readings. The measures introduced included a more efficient traffic light system in the surrounding area and general road improvement measures to increase the traffic flow through the arterial roads in Hamburg. In addition, the measures included the installation of particulate filters in used vehicles. Since 2005, the measures against particulate pollution have not been revised or renewed (status 2020).
In contrast to other major German cities, Hamburg does not have environmental zones in which only low-emission vehicles are allowed to drive. Thus, vehicles with higher emission levels are also allowed to drive into the city centre, which has a negative effect on air quality in Hamburg.
7Contributors
Government Contributor
4 stations
5 Individual Contributors
1 station
1 station

1 station
1 station
1 station
Anonymous Contributor

1 station