Get a monitor and contributor to air quality data in your city.
24.8K people follow this city





AIR QUALITY DATA CONTRIBUTORS
Find out more about contributors and data sources| Index | N/A | |
| Tree pollen | N/A | |
| Grass pollen | N/A | |
| Weed pollen | N/A |
| Weather | Broken clouds |
| Temperature | 55.4°F |
| Humidity | 70% |
| Wind | 8.1 mp/h |
| Pressure | 30 Hg |
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Palm Desert, California | 95 |
| 2 | Aiken, South Carolina | 61 |
| 3 | Casa Grande, Arizona | 61 |
| 4 | Pahrump, Nevada | 61 |
| 5 | Nevada County, California | 55 |
| 6 | Portola, California | 54 |
| 7 | Yucaipa, California | 52 |
| 8 | Hot Springs, South Dakota | 49 |
| 9 | Rapid City, South Dakota | 49 |
| 10 | Carlsbad, New Mexico | 47 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ramona Cir | 45 |
| 2 | Lane D East | 44 |
| 3 | Montebello | 37 |
| 4 | Lincoln Court | 24 |
| 5 | Byron 01 | 21 |
| 6 | Harker Avenue | 20 |
| 7 | 642 Webster Outdoor | 19 |
| 8 | Bryant x Oregon | 19 |
| 9 | Fergus Garber Architects | 18 |
| 10 | Oxford Avenue | 18 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
15
live AQI index
Good
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 15 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 3.6µg/m³ | |
PM2.5 concentration in Palo Alto air currently meets the WHO annual air quality guideline value
| Enjoy outdoor activities | |
| Open your windows to bring clean, fresh air indoors GET A MONITOR |
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturday, Apr 20 | Good 17 AQI US | 78.8° 51.8° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 21 | Good 19 AQI US | 71.6° 51.8° | ||
| Monday, Apr 22 | Good 14 AQI US | 64.4° 51.8° | ||
| Today | Good 15 AQI US | 64.4° 50° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Good 17 AQI US | 60.8° 48.2° | ||
| Thursday, Apr 25 | Good 10 AQI US | 60.8° 51.8° | ||
| Friday, Apr 26 | Good 10 AQI US | 62.6° 48.2° | ||
| Saturday, Apr 27 | Good 12 AQI US | 64.4° 48.2° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 28 | Good 14 AQI US | 62.6° 46.4° | ||
| Monday, Apr 29 | Good 10 AQI US | 60.8° 46.4° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
Air quality in Palo Alto, California receives mixed ratings for PM2.5 and ozone, the two pollutants considered most dangerous in the United States.
PM2.5, or particulate matter that measures less than 2.5 microns in diameter, is small enough to penetrate deep into the lungs, with the smallest particles able to enter the bloodstream. PM2.5 can include dust, dirt, aerosols, and viruses, but it is most commonly associated with combustion-created ash, soot, and chemicals. Motor vehicles and other forms of fossil-fuel combustion in Palo Alto and the greater San Francisco Bay Area directly produces PM2.5. These pollution sources also produce gases that can form PM2.5 as they coagulate (randomly collide to form larger particle clumps).
While PM2.5 is just one of 6 criteria pollutants measured by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), it is estimated to be the leading cause of global health impacts from air pollution.1 Both short-term and long-term exposure has been linked to adverse health effects. In the short term, elevated PM2.5 levels are linked to coughing, asthma attacks, and difficulty breathing as well as exacerbated heart ailments. Long-term exposure, on the other hand, is linked to lung disease, cancer, heart attacks, and early death.
The American Lung Association (ALA) prepares an annual report card for US counties, grading their ability to meet federal standards for short- and long-term pollution. In the most recent 2016 to 2018 monitoring period, the ALA gave Santa Clara County, of which Palo Alto is a part, an “F” for daily PM2.5 pollution and a passing grade for annual PM2.5 pollution.2
Short-term, or daily, pollution is evaluated on a city’s ability to meet the EPA allowance of 3.2 unhealthy days per year. Santa Clara County and Palo Alto both failed to meet this standard, with an average of 10.2 unhealthy days per year. Short term spikes in daily particle pollution are most often associated with winter wood burning and wildfire smoke, the latter of which has been notably on the rise in recent years.
Annual PM2.5 is evaluated based on a city’s ability to average less than 12 μg/m3 over the course of a year. In 2019, Palo Alto averaged a PM2.5 concentration of 6.5 μg/m3, thereby meeting the federal government standard as well as the more stringent World Health Organization (WHO) target of 10 μg/m3.
On a national level, Palo Alto’s short- and long-term PM2.5 levels are considered relatively poor. The greater San Jose, San Francisco, and Oakland, California area was ranked 3rd for worst daily PM2.5 pollution out of 217 metropolitan areas, and 5th for worst annual PM2.5 out of 203 metropolitan areas.
Palo Alto air quality, however, fares slightly better than some of its neighbors. While Palo Alto, as mentioned, averaged an annual PM2.5 concentration of 6.5 μg/m3 in 2019, its neighbors averaged the following PM2.5 concentrations:
In addition to PM2.5, Palo Alto’s ozone levels are also of concern. Ozone is a highly reactive gas pollutant. When inhaled, ozone reacts with our lungs, resulting in a range of respiratory symptoms. Long-term exposure to elevated levels can lead to decreased lung function and increased airway hyperreactivity.
Short-term ozone, like short-term PM2.5, is measured as the number of days which are deemed unhealthy in a year. Santa Clara County averages 2.8 unhealthy ozone yearly. While that meets the federal allowance of 3.2 unhealthy days per year, the presence of some unhealthy days resulted in a “D” ALA grade.
On a national level, the greater San Jose, San Francisco, and Oakland, California area was ranked 8th for high ozone days out of 228 metropolitan areas, experiencing quite a bit more ozone pollution than most locations in the United States.
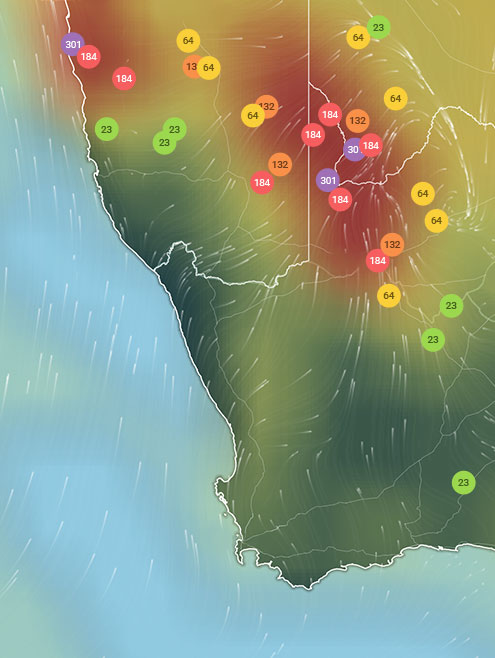
Current air quality levels in Palo Alto are dependent on a combination of factors, including daily emissions, weather, and geography. Just like air is always on the move, so too is air pollution. While trends reveal typical conditions, it is important to check real-time air pollution levels in Palo Alto in order to protect oneself and family from adverse health effects. Refer to the top of this page for live and forecast AQI levels in Palo Alto.
Palo Alto and the greater Santa Clara County have experienced greatly improved air quality over the last two decades. Overall, measures for short-term ozone, short-term PM2.5, and annual PM2.5 have all experienced reduced levels since the turn of the century. These improvements include:
While ozone levels have fallen steadily, both short-term and long-term PM2.5 have seen rising levels since the 2014-2016 monitoring period. These increases in particle pollution are attributed to historic wildfire seasons. 2017, 2018, and 2020 all broke records for acreage burned in California. Many of these catastrophic fires occurred around the Bay Area, resulting in prolonged periods of “unhealthy” air quality in Palo Alto.
The Spare the Air Program was established by the Bay Area Air Quality Management District (BAAQMD) in order to provide residents advance warnings when air quality is forecast to be unhealthy. The program aims to both educate community members about air quality and encourage participation in pollution reduction.3
During the summer months, Spare the Air alerts are most often published for high ozone pollution. This is because ozone is a pollutant formed from gases reacting in sunlight. Without sunlight and heat, ozone formation is not possible. Temperatures over 84 degrees Fahrenheit are typically necessary for ozone to reach elevated levels. Since Palo Alto’s moderate climate is often influenced by cool sea breezes, temperatures higher than this are somewhat rare. As a result, so too are Spare the Air ozone days.
During the winter months, Spare the Air alerts are typically issued for particle pollution as a result of winter wood burning. When an alert is in place, wood burning becomes illegal in Palo Alto. Previously wood-burning bans were exclusive to the winter season. With the rise of frequent and severe wildfires, the wood-burning ban has been extended to include any days year-round when a Spare the Air Alert is in place.
The Bay Area and Palo Alto saw a record number of Spare the Air alerts in 2020 as a result of the historic Lightning Complex Fires. As of October 2020, 47 Spare the Air alerts were issued as compared to 46 for the entire year of 2017 (another historic wildfire season).4
The BAAQMD presides over nine counties of California's San Francisco Bay Area: Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, Napa, San Francisco, San Mateo, Santa Clara, southwestern Solano, and southern Sonoma. “Spare the Air” alerts are a unique feature of BAAQMD. All cities, however, can benefit from such notifications. Use the IQAir air quality forecast to identify when air pollution is expected to reach “unhealthy” or worse levels, in any city globally. Pollution levels forecasted to be “orange,” “red,” “purple,” or “maroon” indicate a Spare the Air alert.
In any given year, California’s most polluted cities tend to be cities most affected by that year’s wildfire season. While wildfires represent a temporary emission source, their impact on monthly and yearly air pollution averages can be severe. Human-driven climate change is expected to further aggravate the intensity of wildfires in the future, by creating warmer and drier conditions. Such a progression is likely to worsen California air quality levels.
California’s fire season notably runs from July through November. Dry conditions, Santa Ana winds, and hot temperatures combine to make an especially volatile environment. Take care to follow Palo Alto live air quality data during these months to stay informed of invisible threats in the air, and guide actions to reduce your exposure.
Use the IQAir Palo Alto air quality map to identify wildfires burning in the area. Fire data is provided by NASA's Fire Information for Resource Management System (FIRMS) satellite observation. The IQAir map and forecast will inform you of wind direction and current air quality levels in the region, as fire data changes.
Warming global temperatures, changing weather patterns, and shifts in plant communities have increased the likelihood wildfires will catch and burn for longer periods of time. Recent years have exhibited early snow melt, record temperature highs, and longer droughts. At the same time, wildfires have been more frequent and severe.
Palo Alto remains a danger for wildfires, particularly the Foothills of Palo Alto.5 The city of Palo Alto, however, has a mitigation strategy that includes:
+ Article Resources
[1] World Health Organization (WHO). (2013). Health effects of particulate matter.
[2] American Lung Association. (2020). State of the Air – 2020.
[3] Bay Area Air Quality Management District (BAAQMD). (2020). About air quality - Spare the Air.
[4] Kirkwood K. (2020, October 10). Bay Area sees record number of Spare the Air alerts in 2020. KTVU.
[5] City of Palo Alto. (2020). Wildfire safety and public safety power shutoffs
84Contributors
Government Contributor
1 station
3 Individual Contributors
2 stations

1 station
1 station
80 Anonymous Contributors

80 stations