Get a monitor and contributor to air quality data in your city.
19.5K people follow this city





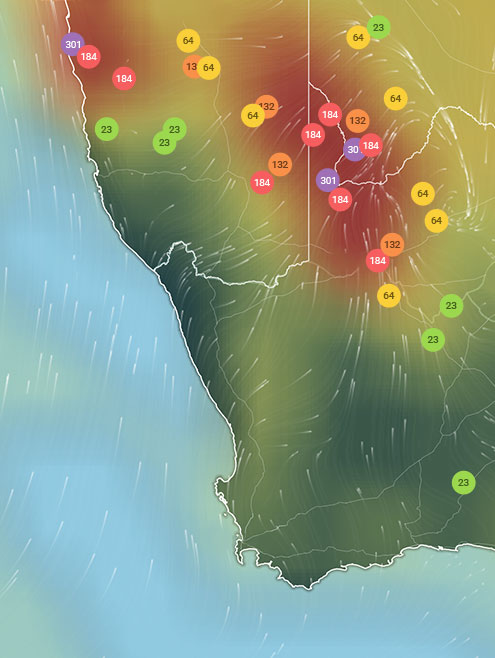
AIR QUALITY DATA CONTRIBUTORS
Find out more about contributors and data sources| Index | Moderate | ||
| Tree pollen | Moderate | ||
| Grass pollen | None | ||
| Weed pollen | None |
| Weather | Clear sky |
| Temperature | 59°F |
| Humidity | 73% |
| Wind | 10 mp/h |
| Pressure | 29.9 Hg |
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | San Bernardino, California | 91 |
| 2 | Corpus Christi, Texas | 79 |
| 3 | Redlands, California | 78 |
| 4 | Yucaipa, California | 78 |
| 5 | Fontana, California | 75 |
| 6 | San Fernando, California | 73 |
| 7 | Beverly Hills, California | 72 |
| 8 | Riverside, California | 72 |
| 9 | Santa Clarita, California | 70 |
| 10 | The Woodlands, Texas | 70 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 811 Smith Road Flex | 45 |
| 2 | Alturas Way | 25 |
| 3 | Scott Valley Swimming & Tennis Club | 25 |
| 4 | Tamalpais Park | 25 |
| 5 | Compton Circle | 24 |
| 6 | Summit Avenue | 24 |
| 7 | Blithedale Terrace | 23 |
| 8 | Laurel Way | 23 |
| 9 | Lower Alcatraz Place | 22 |
| 10 | Meda Lane | 22 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
21
live AQI index
Good
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 21 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 5µg/m³ | |
PM2.5 concentration in Mill Valley air currently meets the WHO annual air quality guideline value
| Enjoy outdoor activities | |
| Open your windows to bring clean, fresh air indoors GET A MONITOR |
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuesday, Apr 16 | Good 15 AQI US | 69.8° 53.6° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 17 | Good 18 AQI US | 62.6° 51.8° | ||
| Thursday, Apr 18 | Good 20 AQI US | 59° 50° | ||
| Today | Good 21 AQI US | 59° 50° | ||
| Saturday, Apr 20 | Good 21 AQI US | 62.6° 50° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 21 | Good 16 AQI US | 62.6° 51.8° | ||
| Monday, Apr 22 | Good 22 AQI US | 59° 53.6° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 23 | Good 16 AQI US | 55.4° 51.8° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Good 14 AQI US | 57.2° 51.8° | ||
| Thursday, Apr 25 | Good 11 AQI US | 55.4° 48.2° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
Mill Valley is located in Marin County in northwestern California, roughly 50 miles west of Napa and 14 miles north of San Francisco. In 2019, Mill Valley averaged a PM2.5 concentration of 5.4 μg/m3, equivalent to a “good” US air quality index (AQI) level and indicating that air quality typically poses little to no health risks to residents.
The city’s frequent rainfall and location adjacent to the ocean and neighboring forests combine to create ideal conditions for clean air. Mill Valley, moreover, has relatively few local emission sources, with a population of only 14,000. It is Mill Valley’s proximity to Silicon Valley, San Francisco, and other Bay area cities that largely affects the amount of pollution dispersed in area.
Sea breezes, or cold air blowing in from the coast, contributes to “marine inversions,” a weather event in which pollutants become trapped in the lower atmosphere. Marine inversions can persist for days or weeks at a time until temperature and weather conditions allow pollutants to dissipate.
According to the EPA’s Air Quality Index Report, Marin county experienced 337 days of “good” air quality, 25 days of “moderate” air quality, and only 1 day of air quality that is considered “unhealthy for sensitive groups” in 2019 — a drastic improvement from ten years earlier, when Marin County experienced 270 days of air quality rated “good,” 91 days of “moderate” air quality, and 4 days of air quality deemed “unhealthy for sensitive groups.”1
Best Places has rated the air quality in Mill Valley 81 out of 100 (100 being the best).2 This rating improves upon the United States national average of 58, achieved by faring relatively well for 2 public health measure for air pollution: respiratory illness risk and cancer risk. Mill Valley air quality achieved a 19.5 per million persons rating for respiratory illness, less than half that of the San Francisco-Oakland Metro area average of 46.9 per million persons. Mill Valley’s cancer risk assessment was 20.7 per million persons, also less than half of the Bay Area’s score of 43.7 per million persons.
Follow real-time and forecast air quality data provided at the top of this page to best understand local air quality conditions and current health risks. Use the Mill Valley air quality forecast to plan outdoor activities for the healthiest times and reduce your daily exposure.
PM2.5 and ozone are the two air pollutants of greatest concern for Mill Valley due to both their prevalence and relatively high risk to health.
PM2.5 is a category of microscopic pollutant particles that measure 2.5 microns. PM2.5 usually includes a combination of particles with different chemical makeups, including:
In Mill Valley, the presence of PM2.5 soot is particularly prominent and dangerous. Soot is formed when carbon in the air combines with either liquid, such as rain, or other gases in a process known as coagulation. Cars and trucks, ships from Port of San Francisco, and local industrial processes all release emissions that may form soot through coagulation. Wildfires represent a natural source of soot and have become increasingly common in recent years. The most common health issues related to soot include:3
Ozone, a gas pollutant and key component of smog, is another key pollutant of concern to Mill Valley air quality. Ozone is created when primary pollutants (typically nitrogen dioxide, or NO2, and volatile organic compounds, or VOCs) are released into the air and react together in the presence of sunlight.
Since warm temperatures are required to initiate the chemical reaction, Mill Valley’s cool temperatures tend to keep ozone levels down. Frequent wind and rain additionally help moderate the buildup of ozone around Mill Valley. Still, the Bay Area’s warmer months (April through October) tend to have conditions that are prone to ozone formation and accumulation, as warmer temperatures accelerate ozone formation. During these months, Mill Valley ozone can become unhealthy, although generally only for short periods of time.
Although Mill Valley tends to be less polluted than more densely populated areas of northwestern California, pollution can drift from one area to another. This is particularly common in the Bay Area, which shares a geographical basin throughout the region that can trap pollutants that originate miles away. Improving air quality locally requires tackling air quality just beyond its city limits.
According to CalFire, the amount of acreage burned by wildfires has increased tenfold since 1950, rising from 0.1 to 1.4 million acres.4 Wildfire frequency and severity is heightened by rising temperatures and decreased rainfall. Hotter temperatures dry out trees and brush, making them easier to ignite. A simple spark can create a wildfire and then quickly spread to other areas when fanned by winds.
Winds blowing in from fires in the San Francisco Bay Area can carry soot and other particulate matter to Mill Valley and surrounding areas. When inhaled, these particulates can cause such health risks as:
As wildfires have a propensity to spread rapidly, they may take days, weeks, or even months to be fully contained. During that time, air pollution in Mill Valley can surge into higher levels of the AQI, making the air unhealthy for sensitive groups to breathe. Daniel Swain, a climate scientist with the Institute of the Environment and Sustainability at the University of California, Los Angeles, states that many of today’s fires will be “going for weeks, if not months, and are going to be generating smoke for weeks, if not months.”
In August 2020, a wildfire erupted in Guerneville, California (64 miles from Mill Valley) and burned over 350,000 acres of land surrounding the Napa, Sonoma, Solano, Lake Tahoe, and Yolo regions. Regional air quality was impacted for weeks.
Despite the increase in local wildfires, recent years have seen air quality improvement in Mill Valley. The number of days with air quality deemed "unhealthy” or “unhealthy for sensitive groups” has been steadily declining over the past 10 years. One factor helping to alleviate air quality is the reduction in stationary sources of air pollution in the San Francisco Bay Area. Power plants in Hunters Point and Potrero Hill closed in 2006 and 2010, which reduced the number of total emissions released in the region. Many industrial businesses have also left the area in recent years, as the cost of land and rent has risen.
While the amount of stationary air pollution sources has decreased in the Bay Area, mobile emission sources like cars, trucks, ships, and construction equipment have remained relatively stable. Despite the reduction in poor air quality days, the number of days with “good” air quality has not significantly improved.
In 1991, the Bay Area Air Quality Management District (BAAQMD) created the Spare the Air program to inform residents when air quality is projected to reach unhealthy levels. The program provides suggestions to reduce individual pollution impacts as well as information on major pollution sources.
The BAAQMD district covers all of Marin, Contra Costa, Alameda, Napa, San Francisco, San Mateo, and Santa Clara counties as well as half of Solano and Sonoma counties.
The BAAQMD also developed Wildfire Air Quality Response Program initiative to help prevent, prepare for, and mitigate future wildfires. The program outlines protective health measures and strategies for wildfire events, and is comprised of 3 different components:5
In 2008, the San Francisco Health Code released Article 38, an environmental justice initiative that requires new residential construction projects to install enhanced ventilation if located in areas where computer models show poor air quality (such as areas near major roadways). The health code is meant to specifically address residents who live in underserved, lower-income neighborhoods that tend to experience heightened levels of air pollution.6 The ordinance is regularly updated to remain in compliance with the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA).
The San Francisco Department of Public Health is additionally working on a project for policy development using data-based evidence as outlined in the Community Risk Reduction Plan (CRRP). The CRRP will provide a community-wide plan for reducing local air pollution emissions and exposures, aiming to further reduce air pollution emissions through more sustainable energy, cleaner transport, and stringent industry standards.
+ Article resources
[1] Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (2020). Air Quality Index Report.
[2] Best Places. (2010). Health in Mill Valley California.
[3] Schiavone R. (2015, April 27). Mill Valley air quality to be concerning for some this week, officials say. Patch.
[4] Petras G, et al. (2018, August 7). California is burning. USA Today.
[5] Bay Area Air Quality Management Department. (2020, August). Wildfire Air Quality Response Program.
[6] City and County of San Francisco. (2020). City performance score card for San Francisco.
24Contributors
24 Anonymous Contributors

24 stations
1 Data source