Get a monitor and contributor to air quality data in your city.
322.4K people follow this city





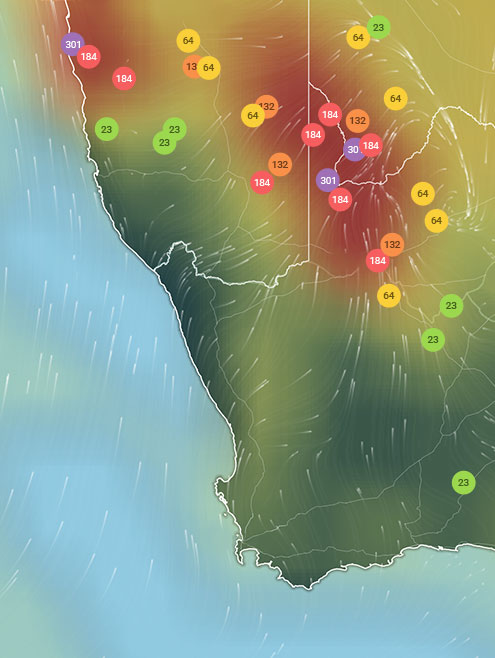
AIR QUALITY DATA CONTRIBUTORS
Find out more about contributors and data sources| Weather | Broken clouds |
| Temperature | 42.8°F |
| Humidity | 77% |
| Wind | 8.1 mp/h |
| Pressure | 29.6 Hg |
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rzeszow, Subcarpathian Voivodeship | 117 |
| 2 | Katowice, Silesia | 87 |
| 3 | Wroclaw, Lower Silesia | 77 |
| 4 | Torun, Kujawsko-Pomorskie | 75 |
| 5 | Krakow, Lesser Poland Voivodeship | 73 |
| 6 | Zielona Gora, Lubusz | 72 |
| 7 | Sopot, Pomerania | 66 |
| 8 | Poznan, Greater Poland | 65 |
| 9 | Lodz, Lodz Voivodeship | 63 |
| 10 | Gdansk, Pomerania | 54 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Warszawa-Tołstoja | 63 |
| 2 | Warszawa-Komunikacyjna | 60 |
| 3 | Warszawa-Ursynów | 54 |
| 4 | Warszawa-Bajkowa | 53 |
| 5 | Warszawa-Targówek | 41 |
| 6 | Zachodnia/Dabrowa | 37 |
| 7 | Powisle | 35 |
| 8 | Warszawa-Chrościckiego | 33 |
| 9 | Wiertnicza | 33 |
| 10 | Warszawa-IMiGW-PIB | 19 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
41
live AQI index
Good
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 41 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 10µg/m³ | |
| PM10 | 17.8µg/m³ | |
| O3 | 45.7µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 19.6µg/m³ | |
| SO2 | 1.4µg/m³ | |
| CO | 0.8µg/m³ | |
PM2.5
x2
PM2.5 concentration in Warsaw is currently 2 times the WHO annual air quality guideline value
| Enjoy outdoor activities | |
| Open your windows to bring clean, fresh air indoors GET A MONITOR |
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday, Apr 22 | Good 31 AQI US | 44.6° 32° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 23 | Moderate 56 AQI US | 48.2° 32° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Moderate 58 AQI US | 42.8° 39.2° | ||
| Today | Good 41 AQI US | 42.8° 39.2° | ||
| Friday, Apr 26 | Moderate 59 AQI US | 53.6° 39.2° | ||
| Saturday, Apr 27 | Good 46 AQI US | 59° 39.2° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 28 | Good 47 AQI US | 62.6° 44.6° | ||
| Monday, Apr 29 | Moderate 58 AQI US | 69.8° 46.4° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 30 | Moderate 70 AQI US | 73.4° 53.6° | ||
| Wednesday, May 1 | Moderate 69 AQI US | 75.2° 53.6° | ||
| Thursday, May 2 | Moderate 75 AQI US | 75.2° 53.6° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
Warsaw is the capital city of Poland and it is also the largest. It is located on the banks of the Vistula River in east-central Poland. The estimated population in 2019 was 1.8 million in the capital itself and over 3.1 million in its entire metropolitan area.
At the beginning of 2021, Warsaw was experiencing “Moderate” air quality with a US AQI figure of 93, according to recommended levels by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The concentrations of the measured pollutants were as follows: PM2.5 - 32 µg/m³, PM10 - 29 µg/m³ and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) - 14 µg/m³. With levels such as these, the advice is to close windows and doors to prevent the ingress of polluted air and those of a sensitive disposition should avoid venturing outside until the air quality gets better.
During 2019, the air quality in Warsaw was mostly “Moderate” for at least nine months of the year, with figures between 12.1 and 35.4 µg/m³. In June and August, the levels were better and classified as “Good” with readings between 10 and 12 µg/m³. During July, Warsaw achieved the WHO target figure of 10 µg/m³ or less.
The city authorities have the ambition to make Warsaw the "Green Capital of Europe". In 2015, the town hall promised "Million Trees for Warsaw". But they ended up with "a million cars" crossing the borders of the city every day which is an increase of almost 2.5 times in 8 years. Without introducing solutions aimed at changing the priorities of the transport policy of the capital city, it will not be possible to reduce the problem of air pollution in Warsaw, because road transport is responsible for most of the smog generated in the city.
Many substances make up air pollution. Poland has a problem with four: large PM10 dust, small PM2.5 dust, nitrogen oxides and benzo (a) pyrene. The names of the "PM10" and "PM2.5" dust come from the size of the particles that compose them: with a diameter of up to 10 or 2.5 micrometres (a human hair is about 50-70 micrometres in diameter). Nitric oxide is a highly reactive and irritating gas, and benzo (a) pyrene is a toxic hydrocarbon.
In Warsaw, the standards of PM10 and PM2.5 poisonous and harmful to human health and life are sometimes exceeded by at least twice, and sometimes even three times. This situation takes place for one-third of the year.
According to the Smog Alert calculator, city dwellers, including non-smokers, "smoke" even a few packets a week. A resident of Warsaw, breathing an average of two hours a day of city air, smokes the equivalent of over 1,200 cigarettes a year.
There are around 1,900 premises in Warsaw which use the cheapest available fuel to heat their homes. Replacing these furnaces should be a priority for the city. The city movements in 2018 won the promise of replacing all of these by the end of 2019. Unfortunately, the target was not reached.
A new subsidy program for the replacement of heat sources and thermal modernisation in private premises was introduced.
The Warsaw authorities have been receiving applications for co-financing the replacement of solid fuel stoves since 2017. However, something or someone is slow in the uptake as in 2017, only 262 subsidies for the replacement of furnaces were provided in Warsaw. For comparison, 6,000 stoves were replaced in 2017 in Kraków, 1,500 in Wroclaw, and 355 in Katowice.
Smog in Warsaw is a year-round problem, and exceedances of the standards also occur in summer, spring and autumn, not only in winter. This is because, according to data, cars are responsible for over half of PM10 emissions in the city. Warsaw should fight both for Warsaw residents to switch from cars to public transport and for bicycles, and to reduce the effects of mass vehicle movement around the city, for example, in the form of dust raised from the streets by vehicle movement. Without such measures, there is no effective fight against air pollution.
The issuance of free tickets for public transportation has been suggested when the smog levels are getting dangerously high. Temporary restrictions on the movement of private cars on certain streets by narrowing the streets by 1 lane and allocating it for temporary parking spaces have also been considered as a possible answer.
The creation of a comprehensive network of bus lanes on the main access streets has been considered. Only punctual public transport will encourage residents to swap their car for public transport.
Park and Ride car parks close to all major railway stations and stops on the access lines to Warsaw and at major interchange junctions are thought to be in the wrong location. The city should use public money to create parking spaces where we want drivers to leave their cars which are on the outskirts of the city and not in the centre.
Limiting free parking for office workers and councillors is something which was also considered. In return, office employees should receive discounts on long-term public transport cards. The idea is to keep traffic out of the city centre by providing Park and Ride facilities on the outer ring roads to encourage commuters to leave their cars there and complete their journey by public transport.
Low- emission public transport needs to be introduced by replacing the old rolling stock with new low-emission replacements.
The creation of interchange connection hubs for public transport would help prevent many vehicles from entering the city centre.
Smog causes many serious diseases: especially of the respiratory system such as lung cancer, asthma, respiratory allergies, infections and inflammation of the respiratory tract, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary embolism and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Cardiovascular diseases which involve destabilisation of the entire system, including, for example, arterial hypertension, ischemic heart disease, disturbances in blood flow through the brain, heart attacks and stroke. Oncological diseases including lung cancer are also common.
In Warsaw, approximately 3,000 people die prematurely every year due to smog-related illnesses. That's more than killed in car accidents across the country!
5Contributors
2 Government Contributors
7 stations
4 Data sources