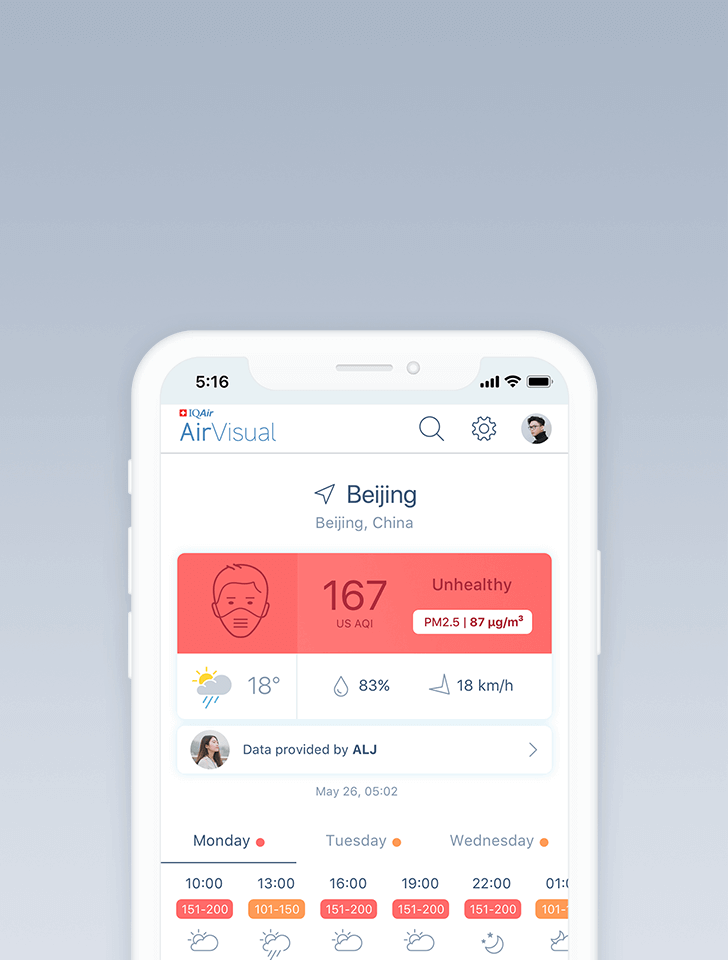
Air quality in Xiangyang
Air quality index (AQI) and PM2.5 air pollution in Xiangyang
9.9K people follow this city
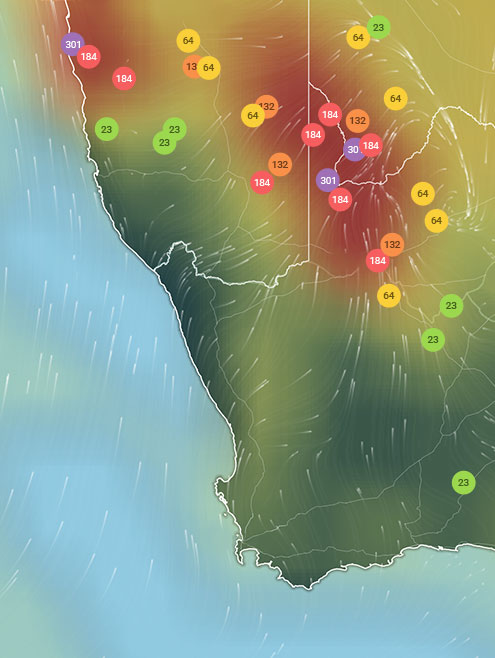
Xiangyang Air Quality Map
Real-time Xiangyang air pollution map
Weather
What is the current weather in Xiangyang?
| Weather | Few clouds |
| Temperature | 62.6°F |
| Humidity | 77% |
| Wind | 4.9 mp/h |
| Pressure | 29.7 Hg |
live aqi city ranking
Real-time China city ranking
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baotou, Inner Mongolia | 424 |
| 2 | Jining, Inner Mongolia | 344 |
| 3 | Hohhot, Inner Mongolia | 321 |
| 4 | Ulanqab, Inner Mongolia | 267 |
| 5 | Ordos, Inner Mongolia | 255 |
| 6 | Yangcun, Tianjin | 168 |
| 7 | Beijing, Beijing | 165 |
| 8 | Tongzhou, Beijing | 164 |
| 9 | Fengrun, Hebei | 160 |
| 10 | Xiangyang, Hubei | 159 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING3D animated air pollution map
live Xiangyang aqi ranking
Real-time Xiangyang air quality ranking
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | High-tech management committee | 164 |
| 2 | Fancheng Xinhua Road | 163 |
| 3 | Xiang cheng yundong lu | 160 |
| 4 | Zhangzhou Aviation Road | 158 |
| 5 | Xiangcheng Longzhong Road | 117 |
| 6 | High-tech Taiziwan | 82 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
159
live AQI index
Unhealthy
Overview
What is the current air quality in Xiangyang?
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Unhealthy | 159 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 71µg/m³ | |
| PM10 | 104.5µg/m³ | |
| O3 | 68µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 21µg/m³ | |
| SO2 | 11.5µg/m³ | |
| CO | 750µg/m³ | |
PM2.5
x14.2
PM2.5 concentration in Xiangyang is currently 14.2 times the WHO annual air quality guideline value
Health Recommendations
What is the current air quality in Xiangyang?
| Avoid outdoor exercise | |
| Close your windows to avoid dirty outdoor air GET A MONITOR | |
| Wear a mask outdoors GET A MASK | |
| Run an air purifier GET AN AIR PURIFIER |
Forecast
Xiangyang air quality index (AQI) forecast
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday, Apr 22 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 139 AQI US | 78.8° 60.8° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 23 | Unhealthy 165 AQI US | 78.8° 60.8° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Unhealthy 151 AQI US | 82.4° 60.8° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 109 AQI US | 82.4° 60.8° | ||
| Today | Unhealthy 159 AQI US | 82.4° 60.8° | ||
| Friday, Apr 26 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 101 AQI US | 86° 62.6° | ||
| Saturday, Apr 27 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 113 AQI US | 87.8° 66.2° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 28 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 107 AQI US | 77° 64.4° | ||
| Monday, Apr 29 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups 112 AQI US | 75.2° 59° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 30 | Moderate 69 AQI US | 59° 55.4° | ||
| Wednesday, May 1 | Moderate 58 AQI US | 69.8° 57.2° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
AIR QUALITY ANALYSIS AND STATISTICS FOR Xiangyang
What is the level of air pollution in Xiangyang?
Xiangyang is a prefecture-level city in the north-western Hubei province in China and the second-largest city in Hubei by population. It was known as Xiangfan from 1950 until 2010. It straddles the Han River which acts as a north-south divide. As a prefecture-level city, it administers 3 districts, 3 county-level cities and 3 counties.
Recently, it has been the policy of the Chines government to urbanise and develop the interior provinces and Hubei is one of them. In 2017 the population had grown to 5.65 million inhabitants of which 3.37 million lived in the metropolitan area.
In the second quarter of 2021, Xiangyang was going through a period of “Unhealthy” air with a US AQI reading of 153. This is in line with the recommendations from the World Health Organisation (WHO). Six of the main pollutants are measured and used as a universal benchmark when determining the level of air pollution. The concentration levels of these six were as follows: PM2.5 - 58.5 µg/m³, PM10 - 51.5 µg/m³, ozone (O3) - 58 µg/m³, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) - 19.5 µg/m³, sulphur dioxide (SO2) - 6.5 µg/m³ and carbon monoxide (CO) - 850 µg/m³.
The advice given to the general public when air pollution is at these elevated levels is to stay indoors as much as possible and close doors and windows to prevent the ingress of more dirty air into the rooms. Consider using an air purifier if you have access to one. Those groups of people who are extra sensitive to pollutants should avoid venturing outside until the air quality improves. The table at the top of this page will help you plan ahead as to when the air is cleaner.
Is the level of air pollution in Xiangyang consistent throughout the year?
Air pollution is very volatile and is affected by many variables so it is easy to see that the level can change very quickly depending on current conditions. Looking at the recently published figures from 2020 on the IQAir website it can be seen that the level of air pollution varies depending on the season of the year. The cleanest time of the year in Xiangyang was during the summer months of June, July and August when the air pollution level was “Moderate” with figures between 12.1 and 35.4 µg/m³. During springtime in March, April and May the pollution level was classed as being “Unhealthy for sensitive groups” with readings between 35.5 and 55.4 µg/m³. The same level occurred during September, just before the onset of autumn. The remaining months were the coldest ones in the year when heating is required in both homes and commercial buildings. From the start of October until around the end of February, the air quality can be called “Unhealthy” with figures between 55.5 and 150.4 µg/m³.
Records of air quality have been kept since 2017 and a slight improvement can be seen, year on year. In 2017 the figure was 64.4 µg/m³ followed by 60.5 µg/m³ in 2018. 2019 saw a tiny improvement at 60.4 µg/m³ whilst in 2020 a noticeable drop was recorded with a figure of 52.5 µg/m³. This low figure could well be artificially low because of the restrictions put in place due to the COVID-19 pandemic when the use of vehicles was curtailed and several manufacturing units closed temporarily.
Where does the air pollution in Xiangyang come from?
It would seem that a lot of the polluted air is caused by dust and dirt blown into the province from Inner Mongolia and Qinghai.
Due to the lack of central heating and chemical industry, in addition to the emissions from coal-fired enterprises such as power plants and the pollution transported from surrounding rural biomass burning activities, vehicle emissions are responsible for the major pollution source affecting the air quality and public health in Xiangyang.
Can air pollution in Xiangyang be reduced?
In recent years, Xiangyang City has focused on the goal of air pollution prevention and control, and the city has overcome difficulties and achieved certain results. In the first half of 2020, the city’s air quality rate was 77.5 per cent, an increase of 19.5 percentage points over the same period in 2019; this year’s total number of excellent days was 141, an increase of 36 days over the same period in 2019, and the air quality improvement rate in the first quarter of 2020 was among 168 key points nationwide.
After the lockdown of city traffic, personnel flow control became the most important aspect. Traffic pollution produces nitrogen monoxide (NO), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), diesel-exhaust particles, and ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), secondary aerosols formed through physical and chemical processes, and pollutants that arise from brake wear, tyre wear and re-suspended particles (e.g., trace metals). There was a notable association between traffic-related air pollution and premature mortality, and the risk of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases increased in residents living close to high-traffic pollution areas.
What difference to our health is there between PM2.5 and PM10?
Both PM10 and PM2.5 come from the family of inhalable particulate matter and have an inclusive relationship. PM2.5 generally accounts for about 70 per cent of PM10. In addition to the difference in diameter, there are also certain differences in the impact on the human body.
PM10 can be directly inhaled into the respiratory tract, but part of it can be excreted through sputum, etc., and it will also be blocked by the villi inside the nasal cavity, which is relatively less harmful to human health. However, the impact of PM10 on visibility and temperature is very obvious.
However, PM2.5 enters the alveoli through the respiratory tract and is deposited in the lungs. At the same time, these particles have strong adsorption capacity and are the "carriers" and "catalysts" of multiple pollutants. Once inside the alveoli, the pollutants can easily enter the bloodstream and travel throughout the body as far as the heart and the brain.
There are about 480 million alveoli in the average human adult body, located at the end of bronchial tubes. When you breathe in, the alveoli expand to take in oxygen. When you breathe out, the alveoli shrink to expel carbon dioxide.
Xiangyang air quality data attribution
1 Data source