Get a monitor and contributor to air quality data in your city.
33.1K people follow this city





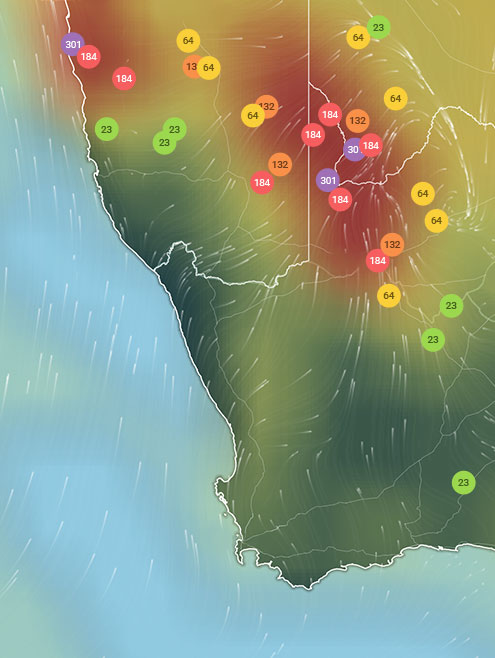
AIR QUALITY DATA CONTRIBUTORS
Find out more about contributors and data sources| Weather | Few clouds |
| Temperature | 69.8°F |
| Humidity | 63% |
| Wind | 6.2 mp/h |
| Pressure | 30 Hg |
| # | city | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Talcahuano, Biobio | 73 |
| 2 | Santiago, Santiago Metropolitan | 71 |
| 3 | Coronel, Biobio | 68 |
| 4 | Quillota, Valparaiso | 66 |
| 5 | Quintero, Valparaiso | 66 |
| 6 | Coyhaique, Aisen | 65 |
| 7 | Concepcion, Biobio | 53 |
| 8 | Puchuncavi, Valparaiso | 50 |
| 9 | Concon, Valparaiso | 45 |
| 10 | Temuco, Araucania | 41 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKING
| # | station | US AQI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SSO Callisto out | 24 |
(local time)
SEE WORLD AQI RANKINGUS AQI
24
live AQI index
Good
| Air pollution level | Air quality index | Main pollutant |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 24 US AQI | PM2.5 |
| Pollutants | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 5.8µg/m³ | |
| NO2 | 7.4µg/m³ | |
PM2.5
x1.2
PM2.5 concentration in Antofagasta is currently 1.2 times the WHO annual air quality guideline value
| Enjoy outdoor activities | |
| Open your windows to bring clean, fresh air indoors GET A MONITOR |
| Day | Pollution level | Weather | Temperature | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuesday, Apr 16 | Good 26 AQI US | 71.6° 62.6° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 17 | Good 24 AQI US | 71.6° 60.8° | ||
| Thursday, Apr 18 | Good 21 AQI US | 69.8° 60.8° | ||
| Today | Good 24 AQI US | 69.8° 60.8° | ||
| Saturday, Apr 20 | Good 48 AQI US | 71.6° 60.8° | ||
| Sunday, Apr 21 | Moderate 55 AQI US | 69.8° 60.8° | ||
| Monday, Apr 22 | Moderate 56 AQI US | 69.8° 60.8° | ||
| Tuesday, Apr 23 | Moderate 51 AQI US | 68° 60.8° | ||
| Wednesday, Apr 24 | Moderate 57 AQI US | 68° 60.8° | ||
| Thursday, Apr 25 | Moderate 58 AQI US | 68° 60.8° |
Interested in hourly forecast? Get the app
Antofagasta is a port city in northern Chile, about 1,100 kilometres north of the capital of Santiago. It is the capital of Antofagasta Province and Antofagasta Region. A census was conducted in 2015 which estimated the population to be approximately 402,000 people.
The quality of the air in September 2021 was “Good” with a US AQI reading of 25. This United States Air Quality Index number is calculated using the levels of six of the most prolific air pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, ozone, carbon monoxide and both sizes of particulate matter, which are PM2.5 and PM10. It can then be used as the metric when comparing air quality in other cities around the world. If data is unavailable for all 6 pollutants, a figure can still be calculated by using what figures there are. For Antofagasta, the only reading was for PM2.5 which was 6.1 µg/m³. This level is below the recommended target figure of 10 µg/m³ which was suggested by the World Health Organisation (WHO). Probably why the air quality is classed as “Good”, although no amount of air pollution is considered to be safe.
With air quality at this level, doors and windows can be safely left open to allow a flow of fresh air into the rooms. All types of outdoor activities can be enjoyed without fear. For up-to-date information as to the state of the air, there is a downloadable app from AirVisual which is available for all operating systems.
The quality of air can and does change very quickly because it is influenced by many factors. Looking back at the published figures from 2020 by IQAir.com, it can readily be seen that the months with the poorest quality air were May, June and July. With respective figures of 12.8, 12.1 and 13.6 µg/m³ the quality was classified as being “Moderate”. Figures between 12.1 and 35.4 µg/m³ are categorised as such. Air quality during the months of April and August could be classified as “Good” with figures of 10.6 and 11.0 µg/m³. The remaining 7 months of the year attained the target figure or less, as recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The target figure being 10 µg/m³ or less.
Looking back to when records were first kept in 2017, the air quality was “Good” with an average annual reading of 10.6 µg/m³. The following year achieved the WHO target with a figure of 9.1 µg/m³. 2019 saw a decline in quality when the figure recorded was 12.2 µg/m³ which put it in the “Moderate” bracket. 2020 saw a return to the WHO target figure with a reading of 9.4 µg/m³. This low figure coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic when many vehicles were no longer in daily use in an attempt to stop the spread of the virus. Many factories and non-essential production units were also required to close which removed their emissions from the atmosphere and therefore, most cities revealed very good figures for air quality.
In this region, the main sources of atmospheric pollutants are associated with mining extraction processes, copper smelters and electricity generation, Particulate Material, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides being the main pollutants emitted.
In the area there are two areas declared saturated by PM10 (Maria Elena and Chuquicamata) and one area declared latent by sulphur dioxide (Chuquicamata). However, the annual averages of PM10 registered in recent years have exceeded the level set in the annual PM10 standard in Calama, Tocopilla and Sierra Gorda, and the first two cities indicated are currently in the process of declaring a zone.
Other pollutants found in the air around the port were arsenic, copper, lead and cadmium. It is thought these originate due to the shipment and disembarkation of minerals to warehouses on the quayside. The average level of arsenic in northern Chile in some locations exceeds 4 times the maximum allowed.
Lung cancer frequency has been progressively increasing; this has been linked to the use of inhaled tobacco and air pollution. In Chile, air pollution has reached alarming levels due to motor vehicle traffic, firewood burning for heating and minerals in urban areas.
An urgent call to the Public Health Department, made the Medical College of Chile and its regional Antofagasta, with the objective that said public department activates health prevention measures as soon as possible, to protect the health of the population of Antofagasta, against the serious and evident contamination with metallic dust from Chilean copper and Bolivian lead and zinc mining concentrates, which continue to affect the streets of the regional capital on a daily basis.
Air pollution has gained recognition and prominence on global agendas. In September 2015, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The central references to air pollution in the Agenda are made under three main target areas;
What are the key facts with air pollution?
1Contributor
Anonymous Contributor

1 station
1 Data source